Nike is on a journey toward sustainability. With the fashion industry significantly contributing to global carbon emissions, who better than Nike to set a new industry standard? The brand embraces the principles of circularity, sourcing materials from post-consumer waste and low-impact alternatives.
 Image Source Nike Move to Zero
Image Source Nike Move to Zero
Nike raises important questions and explores concepts that could be integrated into circular business models, considering various factors such as product recyclability, material selection, green chemistry, and durability.
In the fashion industry, the term circularity generally refers to a sustainable approach to both production and consumption. Goals are to minimize waste, extend product life cycles, and balance sustainability with economic efficiency. Circular strategies can focus on various aspects, including recycling and upcycling, resale and reuse, sustainable materials, ethical production, and more.
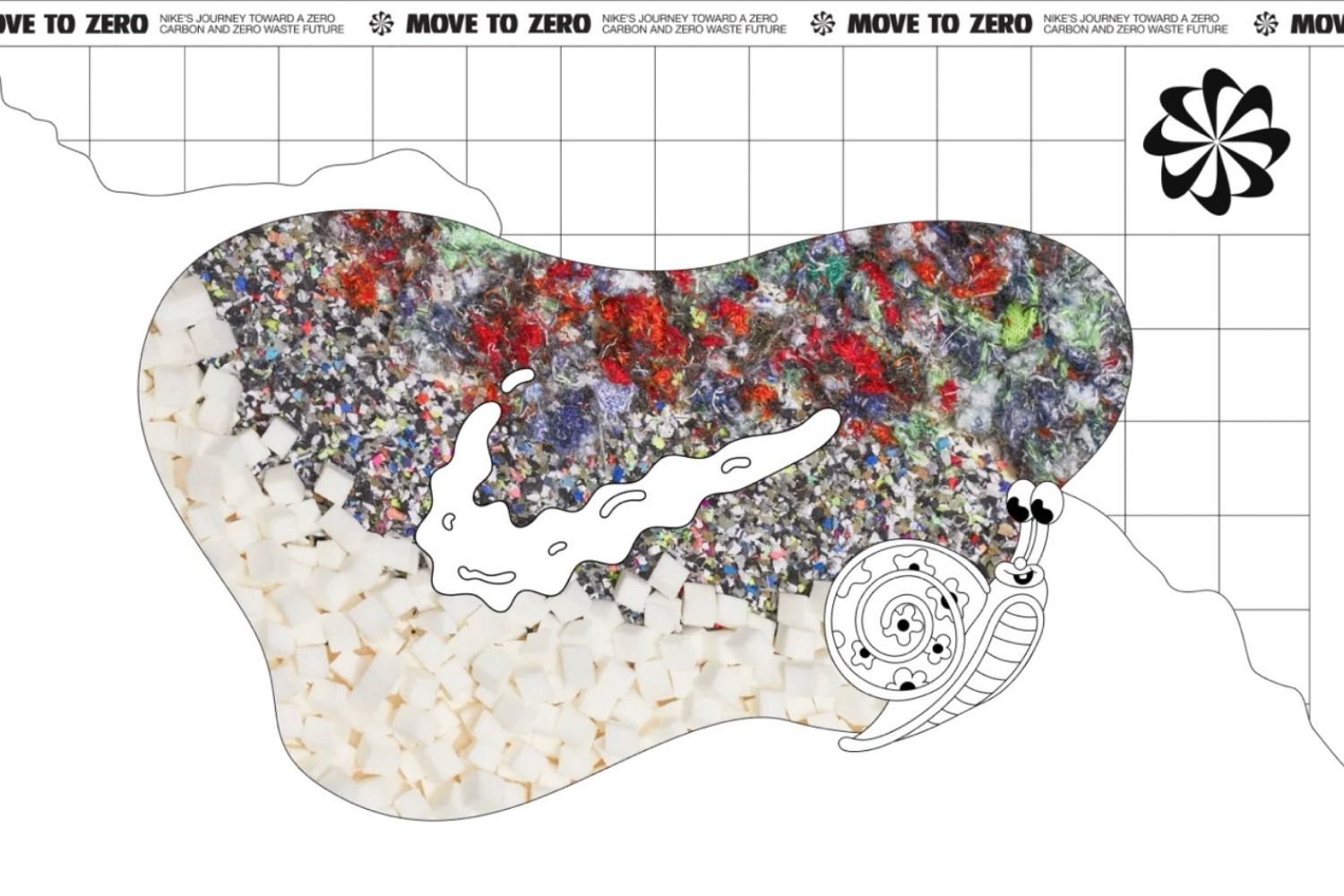
Nike Material Choices
Nike’s journey toward sustainability begins with its materials. By shifting sourcing practices, the company aims to move away from the traditional take-make-dispose model and transition into a circular, renewable system.
Nike Flyleather is a prime example of this effort—made with at least 50% recycled leather; it is used in their sustainable apparel line. Since separating different fibers for recycling can be complex, Nike is exploring using mono-materials (products made from a single material) to simplify the process and improve recyclability.
 Image Source Nike Move to Zero
Image Source Nike Move to Zero
The Swoosh Brand also utilizes brand case studies to shape and refine its approach. One of the brand’s biggest design challenges is creating products with a lower environmental impact that can be easily recycled.
Additionally, Nike is raising important questions about biodegradability, alternative uses for waste in fashion and other industries, and potential partnerships that could help build an ecosystem of sustainability advocates, ultimately facilitating a fully circular model.
 Image Source Nike Move to Zero
Image Source Nike Move to Zero
Nike also looks to Levi Strauss & Co. as an example to follow. Levi’s collects used denim of all brands and colors across the U.S. and Canada, repurposing it into insulation for low-income housing in exchange for a 20% discount on new Levi’s denim purchases. The brand has also introduced a vintage line based on circular principles, questioning whether items can increase in value the longer they are in circulation.
Nike Grind
 Image Source Nike Grind
Image Source Nike Grind
Twenty-five years ago, Nike pioneered a zero-waste strategy with Nike Grind, an initiative that collects discarded shoes and transforms them into basketball courts with a soft, rubber-like surface. Last year alone, Nike and Converse repurposed 3 million pounds of waste into sports and community projects.
Avoiding waste
By designing products with the end of their lifecycle in mind, Nike aims to improve recyclability and repurpose used materials. However, the brand is taking it a step further by setting goals to minimize or eliminate waste throughout the production process. Concepts like 3D-printed products and made-to-order models are being explored to help reduce industry waste.
Recognizing the Value of Components
Designing products that can easily be taken apart and recycled could be a great way to gather valuable resources for new products. However, the question remains: what tools are needed to deconstruct the product? What chemical processes are required to break down adhesives? And who will be responsible for this labor-intensive process?
 Image Source Nike Move to Zero
Image Source Nike Move to Zero
Nike also highlights key questions: Will the consumer be responsible for recycling? Will the product need to be sent back to the manufacturer? Or will this create an entirely new third-party industry dedicated to recycling? These are all models and questions being considered as the fashion industry moves toward sustainability.
The Chemistry
Nike is looking into the chemistry of its materials and processes, aiming to achieve zero discharge of hazardous substances. Toxic chemicals can be used in manufacturing materials or produced as byproducts of the process. This waste can include anything from arsenic and chromium to sequins and rhinestones. Toxic materials or components can be risky because they can contaminate water sources, affect the food supply, and, as a consequence, poison humans if consumed.
 Image Source Nike Move to Zero
Image Source Nike Move to Zero
What is ChemFORWARD?
ChemFORWARD is a non-profit organization that collaborates with governments and other NGOs to ensure safety, ChemFORWRAD tracks and tests products for toxic chemicals. They work to identify hazardous chemical sources and waste management, partnered with brands like Nike, Apple, H&M, and Google, among many others. Nike’s collaboration with Roadmap to Zero also ensures a safe, chemical-free environment for production as the brand transitions toward a circular economy and is a testimony to Nike's commitment to professional ethics.
 Image Source Nike Move to Zero
Image Source Nike Move to Zero
Can Nike Be Sustainable?
Nike’s sustainability initiatives paint a promising picture of a fashion giant striving to minimize its environmental footprint. The brand actively tackles key challenges circularly from material innovation to waste reduction and green chemistry. The introduction of mono-materials, the Nike Grind initiative, and collaborations with organizations like ChemFORWARD and Roadmap to Zero all signal a commitment to change.
 Image Source Nike Move to Zero
Image Source Nike Move to Zero
However, the question remains: Is this enough? While Nike’s transparency and efforts toward sustainability are commendable, the brand still operates within an industry built on mass production and overconsumption. Concepts like made-to-order manufacturing and full product recyclability are being explored, but how quickly will they become the norm?
Will these sustainable practices outweigh the sheer scale of Nike’s global production?
Read more about Nike's journey toward sustainability and circularity in our Reflawn News!
Can Nike be sustainable?
Nike is working toward a circular economy by sourcing low-impact materials, recycling post-consumer waste, and minimizing production waste. The brand is also exploring recyclable product designs, green chemistry, and alternative business models that reduce environmental impact.
What is Circularity?
Circularity in fashion and sneakers refers to a sustainable approach to production and consumption. It aims to minimize waste and extend the life cycle of items, emphasizing both sustainability and economic efficiency. Circular approaches focus on key areas such as recycling / upcycling, resale / reuse, sustainable materials, ethical production and more.
What is Circularity at Nike?
Nike is taking steps toward circularity by sourcing materials from post-consumer waste and low-impact alternatives. The brand explores innovative concepts and raises key questions about integrating circular business models, focusing on factors such as product recyclability, material selection, green chemistry, durability, and more.
What materials are sustainable at Nike?
Nike has incorporated the use of recycled materials like FlyLeather and recycled polyster from plastic bottles. Nike is also working with Nike Grind to create basketball courts for vulnerable communities.
What is Nike Move to Zero?
Nike Move to Zero is the brand’s initiative to achieve zero carbon emissions and zero waste across its supply chain and products. It’s Nike’s long-term commitment to sustainability and creating a circular economy in fashion.

.png&w=3840&q=75)




.jpg&w=3840&q=75)
