Fashion brand Gap has entered the Circular Economy with their attempts at sutainability and responsible production. The Circularity Gap Report 2024, developed by the Circle Economy Foundation in collaboration with Deloitte, presents a comprehensive analysis of the global circular economy’s current state and offers a roadmap for transformative change.

The Global Stage
The Circularity Gap Report 2025 highlights the urgent need for a systemic shift toward a circular economy to address the escalating challenges of climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution.
It reveals a stark reality: global material extraction has tripled over the last fifty years, with per capita consumption increasing significantly, driven by urbanisation, GDP growth, and rising affluence.
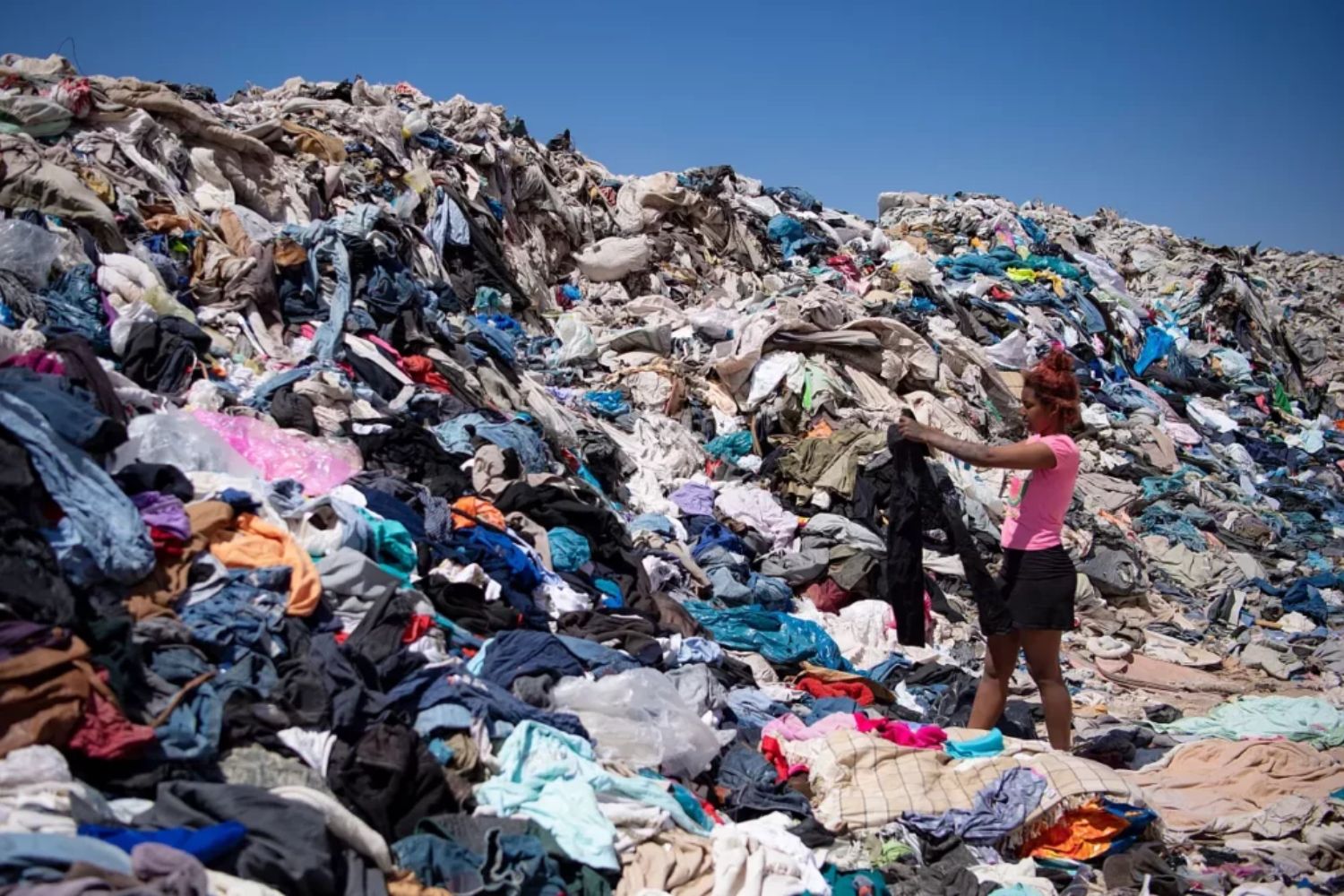

This unsustainable growth is a major cause of the environmental crisis, contributing to two-thirds of greenhouse gas emissions and over 90% of biodiversity loss and water scarcity.
The report points out that people in high-income countries consume six times more materials per person than those in lower-income countries.
Regions like the European Union and the United States use more than half of the world's materials while only making up 10% of the global population. This imbalance shows that industries in wealthier countries need to cut back on consumption, while those in poorer countries should increase it to develop necessary infrastructure and services.

The report identifies important areas for action, urging industries to adopt circular practices. The Circularity Indicator Set offers a framework to understand material flows in the global economy, distinguishing between circular (reused) and linear (wasted) flows.
It emphasises the need for better management of materials to maximise circularity and minimise waste.
Sustainability at Gap
Sustainability, in the context of the Circularity Gap Report, refers to the ability to meet present needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. It emphasises the importance of using resources efficiently and responsibly to minimise environmental impact, reduce waste, and preserve ecosystems.
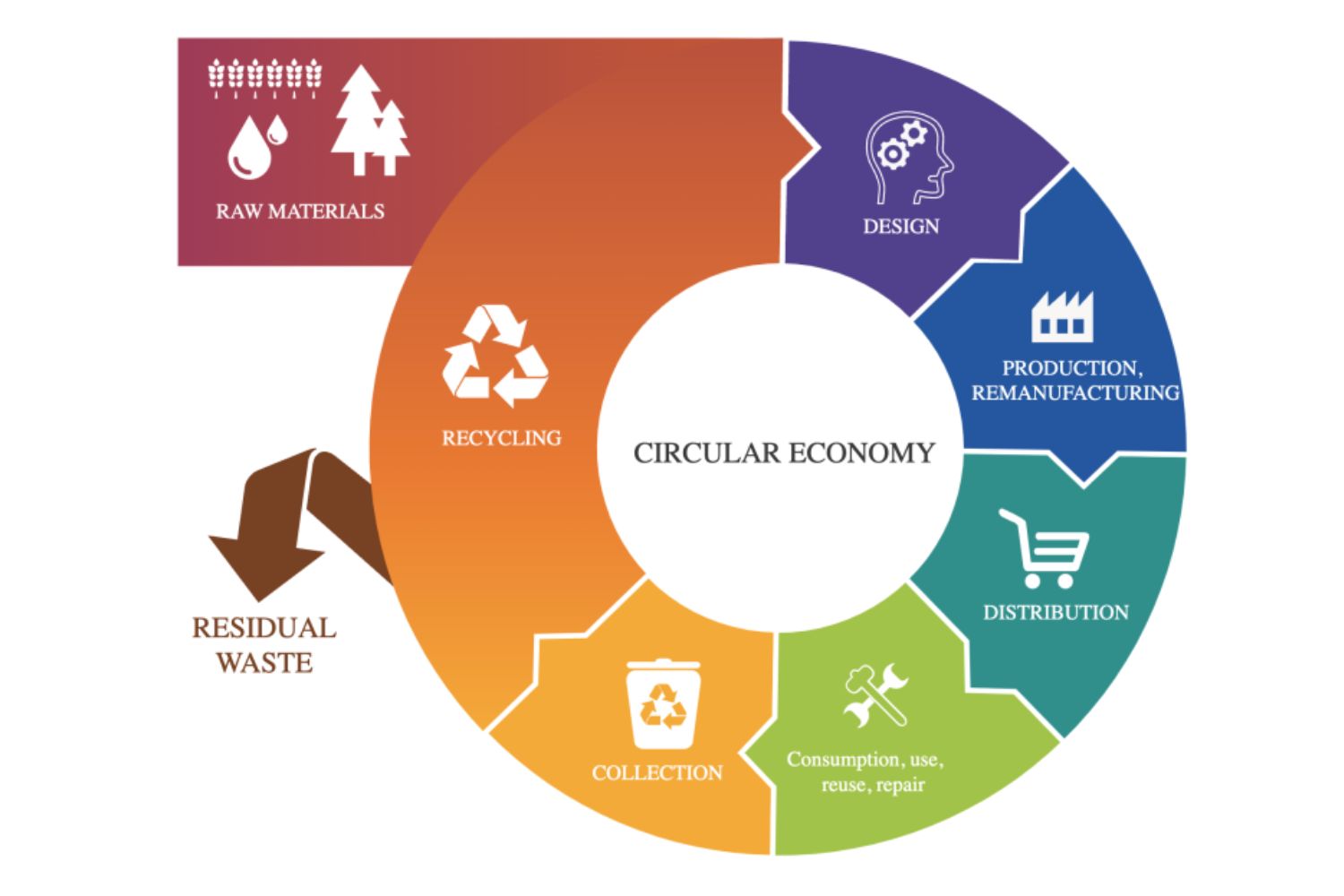
The "gap" in the Circularity Gap Report represents the difference between our current linear economy. Resources are extracted, used, and then discarded, and a fully circular economy, where resources are reused, recycled, and kept in use for as long as possible. The report highlights that the world is currently only about 6.9% circular, meaning that a significant portion of natural resources is wasted or not reused effectively.
Final Thoughts
The Circularity Gap Report 2024 is both a mirror and a map. It reflects the unsustainable path we are on but also points toward achievable, data-backed solutions. The shift to a circular economy won’t happen overnight—but with targeted action, we can bridge the growing gap between what we use and what the planet can sustain.
It’s time to stop treating resources as infinite and start seeing circularity as a necessary blueprint for the future.
All images: GAP
What is the Circular Economy and why does it matter?
The circular economy aims to keep resources in use for as long as possible through reuse, repair, recycling, and regeneration. It addresses urgent issues like climate change and biodiversity loss by reducing material waste and consumption.
What does the Circularity Gap Report 2024 reveal?
It shows that only about 6.9% of the global economy is circular. Material use has tripled in 50 years, contributing to most greenhouse gas emissions and biodiversity loss. High-income countries consume far more than low-income ones, highlighting global imbalances.
How is Gap involved in the circular economy?
Gap has begun adopting sustainable and circular practices, such as using recycled materials, designing longer-lasting products, and reducing waste across its supply chain.







